Eastern Spadefoot
Eastern spadefoot is a small to medium-sized, stout-bodied toad found in the eastern United States.
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Amphibia |
| Order | Anura |
| Family | Scaphiopodidae |
| Genus | Scaphiopus |
| Scientific Name | Scaphiopus holbrookii |
| Size | 1.6 – 3.1 in (4 – 8 cm) |
| Color | Tan or yellowish to dark brown with two vertical lines on the upper surface in an hourglass shape; eyes are bright yellow |
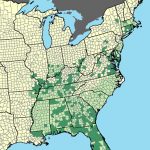
| Distribution | Eastern United States |
| Habitat | Sandy, loose soils in wooded or unwooded terrain; suburban and agricultural areas; breeding habitats include shallow, fishless, temporary ponds and marshes |
| Diet | Ants, beetles, flies, caterpillars, spiders, millipedes, other invertebrates |
| Breeding Season | No defined breeding season, but usually spring and mid-summer |
| Mode of Reproduction | Oviparous (egg laying) |
| Clutch Size | Around 200 eggs or more |
| Incubation Period | 1 to 7 days |
| Metamorphosis Period | 14 to 63 days |
| Reproductive Age | Around 2 years of age |
| Average Lifespan | 12.3 years in captivity |
| IUCN Conservation Status | Least Concern |
Eastern Spadefoot Pictures Gallery
- Eastern Spadefoot Frog
- Eastern Spadefoot Images
- Eastern Spadefoot Photos
- Eastern Spadefoot Pictures
- Eastern Spadefoot Range
- Eastern Spadefoot
- Eastern Spadefoots
- Scaphiopus Holbrookii
Published on April 21st 2017 by staff under Toads. Article was last reviewed on 30th September 2019.